Ankylosing Spondylitis (AS)
Book an appointment Book an appointmentUnderstanding is the first step to health
Common symptoms?

Chronic Back Pain
Typically starts in the lower back and buttocks, worsening with rest and improving with movement.

Morning Stiffness
Common in the spine, hips, and sacroiliac joints, lasting for over 30 minutes.

Reduced Flexibility
Decreased spinal mobility, leading to difficulty bending or twisting the back.

Enthesitis
Pain and swelling where tendons and ligaments attach to bones, particularly at the heel (Achilles tendinitis) or under the feet (plantar fasciitis).

Fatigue
Persistent tiredness and lack of energy, which can impact daily activities.

Peripheral Joint Involvement
In some cases, AS affects other joints like the hips, shoulders, and knees.
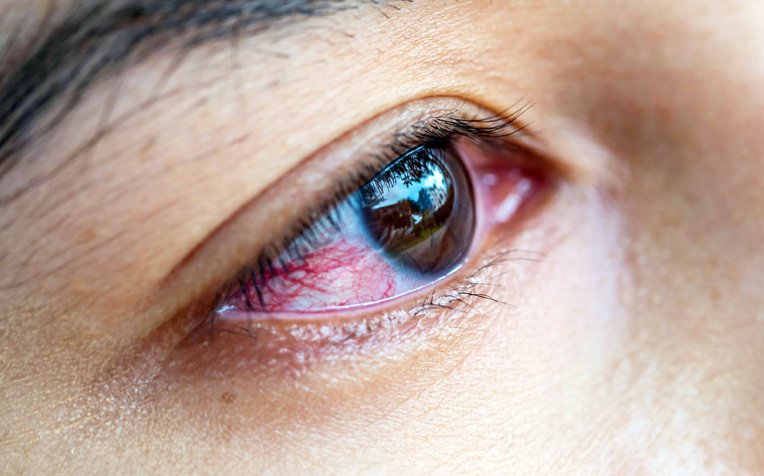
Uveitis
Inflammation of the eye, leading to redness, pain, and sensitivity to light.

Loss of Spinal Mobility
Over time, inflammation can cause fusion of the vertebrae, leading to a rigid spine (bamboo spine).
How is the diagnosis done?

- Medical History and Physical Exam: The doctor will evaluate symptoms like chronic back pain, stiffness, and a family history of AS or other autoimmune diseases.
- Imaging:
-X-rays: The primary diagnostic tool for AS, showing characteristic changes in the sacroiliac joints and spine (e.g., joint space narrowing, bone spurs, and possible spinal fusion).
-MRI: Useful in detecting early changes before they show up on X-rays, particularly inflammation in the sacroiliac joints - Blood Tests:
-HLA-B27: A genetic marker present in about 90% of individuals with AS. While not diagnostic on its own, it is strongly associated with the disease.
-Inflammatory Markers: Elevated C-Reactive Protein (CRP) and Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate (ESR) indicate ongoing inflammation, though they are not specific to AS.
-Physical Function Tests: The Schober test and Chest expansion test are used to assess spinal flexibility and chest mobility, respectively. - Clinical Criteria:
-ASAS (Assessment of SpondyloArthritis International Society) Criteria: These criteria help to diagnose spondyloarthritis and include factors such as clinical presentation (back pain, morning stiffness), radiographic changes (e.g., sacroiliitis on X-ray), and genetic markers like HLA-B27.
-ASAS classification criteria are often used to determine whether a person meets the diagnostic criteria for AS. - New York Criteria: The New York criteria are used to diagnose ankylosing spondylitis based on clinical symptoms and radiographic evidence. They include:
-Clinical Features: Chronic low back pain, limited spinal motion, and a positive family history.
-Radiographic Features: Evidence of sacroiliitis on X-ray (e.g., joint space narrowing, sclerosis, and fusion).
-MCSI (Maksymowych Clinical Spondylitis Index): This tool helps assess disease activity by evaluating symptoms such as spinal pain, stiffness, and overall mobility.
Why is Early Diagnosis Important?

- Preventing Spinal Fusion: Early diagnosis and treatment can help prevent or slow the fusion of spinal vertebrae, preserving spinal mobility and function.
- Improving Quality of Life: With early management, pain and stiffness can be reduced, improving the ability to perform daily activities.
- Managing Inflammation: Untreated AS can cause significant inflammation, leading to long-term damage to joints and tissues.
- Slowing Disease Progression: Early intervention with medications, especially biologics, can help slow or halt disease progression.
- Avoiding Complications: AS can lead to complications like osteoporosis, heart disease, or spinal deformities, all of which can be mitigated with prompt treatment.
Treatment for options AS

- Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs): First-line treatment to reduce pain and inflammation. Common options include ibuprofen, naproxen, and diclofenac.
- Tumor Necrosis Factor (TNF) Inhibitors: Biologic medications like Infliximab, Adalimumab, and Etanercept are highly effective in reducing inflammation and improving symptoms, especially in severe cases.
- Interleukin-17 (IL-17) Inhibitors: Secukinumab is another biologic that targets a specific immune pathway involved in AS.
- Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs (DMARDs):
Sulfasalazine or Methotrexate can be used for peripheral joint involvement but are less effective for spinal symptoms. - Corticosteroids: Oral steroids are generally avoided due to potential side effects, but they may be used for short-term flare-ups or for enthesitis.
- Physical Therapy: Exercises to improve flexibility, strengthen muscles, and maintain posture can help manage symptoms and prevent deformities.
- Surgery: In rare cases, surgery may be needed for severe joint damage or to correct spinal deformities.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Maintaining a healthy weight, practicing good posture, and engaging in regular physical activity can help reduce symptoms and maintain joint function.
Possible outcomes

- Variable Disease Course: The severity and progression of AS vary greatly among individuals. Some may experience mild symptoms with minimal disability, while others may have more severe disease leading to spinal fusion and disability.
- Joint Damage: With effective treatment, most people with AS can manage pain and maintain function, but in severe cases, joint damage and spinal deformities can occur.
- Long-Term Disability: Untreated or poorly controlled AS can lead to long-term disability, especially due to spine stiffness and reduced mobility.
- Life Expectancy: While AS does not typically reduce life expectancy, it can lead to complications like cardiovascular disease, respiratory issues, or osteoporosis, which may affect overall health.
- Comorbidities: AS is associated with an increased risk of heart disease, inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), and osteoporosis, all of which may affect prognosis. Early diagnosis and appropriate treatment can help mitigate these risks.
Disease assesment methods
Several tools are used to assess disease activity and severity in ankylosing spondylitis:
BASDAI (Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Index):
The BASDAI assesses disease activity based on six factors: fatigue, spinal pain, joint pain/swelling, localized tenderness, and morning stiffness. It is scored from 0 (no symptoms) to 10 (severe symptoms). Low Disease Activity: BASDAI ≤ 4High Disease Activity: BASDAI > 4
BASFI (Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Functional Index):
The BASFI measures functional impairment and spinal mobility in people with AS. It includes questions about walking ability, dressing, bending, and daily activities. A higher score indicates greater disability. This score helps guide treatment decisions and monitor disease progress.
ASDAS (Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Score)
Measures the severity of ankylosing spondylitis (AS). It considers factors like pain, stiffness, and inflammation. ASDAS ranges: <1.3: Inactive disease 1.3 - 2.1: Moderate activity 2.1 - 3.5: High activity >3.5: Very high activity
These scoring systems are helpful for tracking disease progression, determining the effectiveness of treatment, and guiding clinical management of ankylosing spondylitis. Regular assessments are key to ensuring optimal care and minimizing long-term disability.
Common symptoms?

Chronic Back Pain
Typically starts in the lower back and buttocks, worsening with rest and improving with movement.

Morning Stiffness
Common in the spine, hips, and sacroiliac joints, lasting for over 30 minutes.

Reduced Flexibility
Decreased spinal mobility, leading to difficulty bending or twisting the back.

Enthesitis
Pain and swelling where tendons and ligaments attach to bones, particularly at the heel (Achilles tendinitis) or under the feet (plantar fasciitis).

Fatigue
Persistent tiredness and lack of energy, which can impact daily activities.

Peripheral Joint Involvement
In some cases, AS affects other joints like the hips, shoulders, and knees.

Uveitis
Inflammation of the eye, leading to redness, pain, and sensitivity to light.

Loss of Spinal Mobility
Over time, inflammation can cause fusion of the vertebrae, leading to a rigid spine (bamboo spine).
How is the diagnosis done?

- Medical History and Physical Exam: The doctor will evaluate symptoms like chronic back pain, stiffness, and a family history of AS or other autoimmune diseases.
- Imaging:
-X-rays: The primary diagnostic tool for AS, showing characteristic changes in the sacroiliac joints and spine (e.g., joint space narrowing, bone spurs, and possible spinal fusion).
-MRI: Useful in detecting early changes before they show up on X-rays, particularly inflammation in the sacroiliac joints - Blood Tests:
-HLA-B27: A genetic marker present in about 90% of individuals with AS. While not diagnostic on its own, it is strongly associated with the disease.
-Inflammatory Markers: Elevated C-Reactive Protein (CRP) and Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate (ESR) indicate ongoing inflammation, though they are not specific to AS.
-Physical Function Tests: The Schober test and Chest expansion test are used to assess spinal flexibility and chest mobility, respectively. - Clinical Criteria:
-ASAS (Assessment of SpondyloArthritis International Society) Criteria: These criteria help to diagnose spondyloarthritis and include factors such as clinical presentation (back pain, morning stiffness), radiographic changes (e.g., sacroiliitis on X-ray), and genetic markers like HLA-B27.
-ASAS classification criteria are often used to determine whether a person meets the diagnostic criteria for AS. - New York Criteria: The New York criteria are used to diagnose ankylosing spondylitis based on clinical symptoms and radiographic evidence. They include:
-Clinical Features: Chronic low back pain, limited spinal motion, and a positive family history.
-Radiographic Features: Evidence of sacroiliitis on X-ray (e.g., joint space narrowing, sclerosis, and fusion).
-MCSI (Maksymowych Clinical Spondylitis Index): This tool helps assess disease activity by evaluating symptoms such as spinal pain, stiffness, and overall mobility.
Why is Early Diagnosis Important?

- Preventing Spinal Fusion: Early diagnosis and treatment can help prevent or slow the fusion of spinal vertebrae, preserving spinal mobility and function.
- Improving Quality of Life: With early management, pain and stiffness can be reduced, improving the ability to perform daily activities.
- Managing Inflammation: Untreated AS can cause significant inflammation, leading to long-term damage to joints and tissues.
- Slowing Disease Progression: Early intervention with medications, especially biologics, can help slow or halt disease progression.
- Avoiding Complications: AS can lead to complications like osteoporosis, heart disease, or spinal deformities, all of which can be mitigated with prompt treatment.
Treatment for options AS

- Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs): First-line treatment to reduce pain and inflammation. Common options include ibuprofen, naproxen, and diclofenac.
- Tumor Necrosis Factor (TNF) Inhibitors: Biologic medications like Infliximab, Adalimumab, and Etanercept are highly effective in reducing inflammation and improving symptoms, especially in severe cases.
- Interleukin-17 (IL-17) Inhibitors: Secukinumab is another biologic that targets a specific immune pathway involved in AS.
- Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs (DMARDs):
Sulfasalazine or Methotrexate can be used for peripheral joint involvement but are less effective for spinal symptoms. - Corticosteroids: Oral steroids are generally avoided due to potential side effects, but they may be used for short-term flare-ups or for enthesitis.
- Physical Therapy: Exercises to improve flexibility, strengthen muscles, and maintain posture can help manage symptoms and prevent deformities.
- Surgery: In rare cases, surgery may be needed for severe joint damage or to correct spinal deformities.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Maintaining a healthy weight, practicing good posture, and engaging in regular physical activity can help reduce symptoms and maintain joint function.
Possible outcomes

- Variable Disease Course: The severity and progression of AS vary greatly among individuals. Some may experience mild symptoms with minimal disability, while others may have more severe disease leading to spinal fusion and disability.
- Joint Damage: With effective treatment, most people with AS can manage pain and maintain function, but in severe cases, joint damage and spinal deformities can occur.
- Long-Term Disability: Untreated or poorly controlled AS can lead to long-term disability, especially due to spine stiffness and reduced mobility.
- Life Expectancy: While AS does not typically reduce life expectancy, it can lead to complications like cardiovascular disease, respiratory issues, or osteoporosis, which may affect overall health.
- Comorbidities: AS is associated with an increased risk of heart disease, inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), and osteoporosis, all of which may affect prognosis. Early diagnosis and appropriate treatment can help mitigate these risks.
Disease assesment methods
Several tools are used to assess disease activity and severity in ankylosing spondylitis:
BASDAI (Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Index):
The BASDAI assesses disease activity based on six factors: fatigue, spinal pain, joint pain/swelling, localized tenderness, and morning stiffness. It is scored from 0 (no symptoms) to 10 (severe symptoms). Low Disease Activity: BASDAI ≤ 4High Disease Activity: BASDAI > 4
BASFI (Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Functional Index):
The BASFI measures functional impairment and spinal mobility in people with AS. It includes questions about walking ability, dressing, bending, and daily activities. A higher score indicates greater disability. This score helps guide treatment decisions and monitor disease progress.
ASDAS (Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Score)
Measures the severity of ankylosing spondylitis (AS). It considers factors like pain, stiffness, and inflammation. ASDAS ranges: <1.3: Inactive disease 1.3 - 2.1: Moderate activity 2.1 - 3.5: High activity >3.5: Very high activity
These scoring systems are helpful for tracking disease progression, determining the effectiveness of treatment, and guiding clinical management of ankylosing spondylitis. Regular assessments are key to ensuring optimal care and minimizing long-term disability.
Frequently
asked questions
Wondering what could be causing your symptoms?
Chat with our virtual assistant to understand your current health status better.
Check your symptoms Check your symptoms



